
Answerįind the difference between 7,214 and 2,049.įind the difference between 56,108 and 52,911. In division without remainder, or exact division, the answer is a whole number. A factor is a whole number that can be divided evenly into another. An example of a well known irrational number is pi which as we all know is 3.14 but if we look deeper at it, it is actually 3.14159265358979323846264338327950288419.and this goes on for somewhere around 5 trillion digits Real Numbers Here is another category where some other of the number classifications will fit. Answerįind the difference between 1,005 and 314.įind the difference between 72,085 and 16. A prime number is a whole number greater than 1 whose only factors are 1 and itself.

The word "from" means "beginning at." Thus, 63 from 92 means beginning at 92, or 92 - 63.įind the difference between 47 and 21. In fact, one of the curious and useful facts that you need to learn about numbers is that any number that ends in five or zero like these ones, is a multiple of five.\) Answerįor the following problems, perform each subtraction. So 10 is a multiple of five and so is 15, and so are 20 and 25. Examples: 0, 7, 2 are all whole numbers (But numbers like, 1.1 and 5 are not whole numbers.) Counting Numbers Counting Numbers are Whole Numbers, but without the zero. Because all of the numbers down the right side after five, are multiples of five. For example, if we were looking for multiples of five, we could look at a five times table. Similar to real numbers and whole numbers, a fractional number also holds some of the important properties. And if three times five equals 15, then we can say that the product of three and five equals 15.Ī multiple is a number, that is the product of a certain whole number and another whole number. Example: If 3/4 is a fraction, then 3 is the numerator and 4 is the denominator. Also, negative numbers are not whole numbers. Whole numbers are located on the right side of the number line.
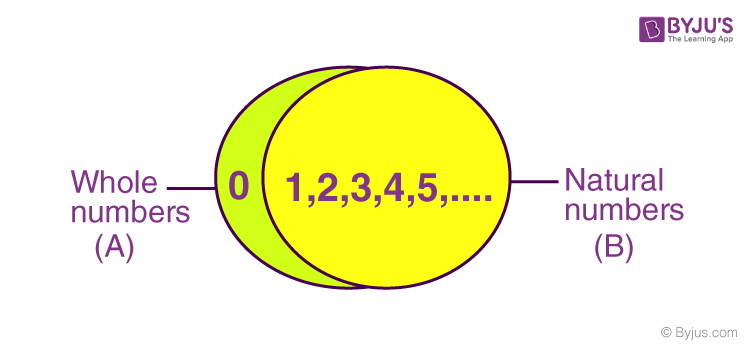
For example, the product of two and 10 is 20. if 0 is included in natural numbers, then it is known as Whole Numbers. Most properties of whole numbers are applicable only for addition and multiplication. In other words, natural numbers are a set of all the whole numbers excluding 0. Properties of whole numbers are closure property, commutative, associative, distributive and identity. Product, is the answer found when numbers are multiplied together. The natural numbers include the positive integers (also known as non-negative integers) and a few examples include 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6. For example there is no whole number that is. The numbers one, two, three and six are all factors of six. In the set of whole numbers, no answer is available when you subtract a number from a number smaller than itself. So, the numbers one and six are also factors of six. For example, 0 is a whole-number but it is not a natural number. But two isn’t a factor of seven, and neither is three, because if we divide seven by two or three we get one left over. 5) All whole-numbers are not natural numbers. So the numbers two and three, are factors of six. For example, the number six can be divided by two, exactly three times or in other words, two times three equals six. An example of a well known irrational number is pi which as we all know is 3.14 but if we look deeper at it, it is actually 3.14159265358979323846264338327950288419. Whole Numbers - The set of Natural Numbers with the number 0 adjoined. Composite Number - A natural number greater than 1 which has more factors than 1 and itself.
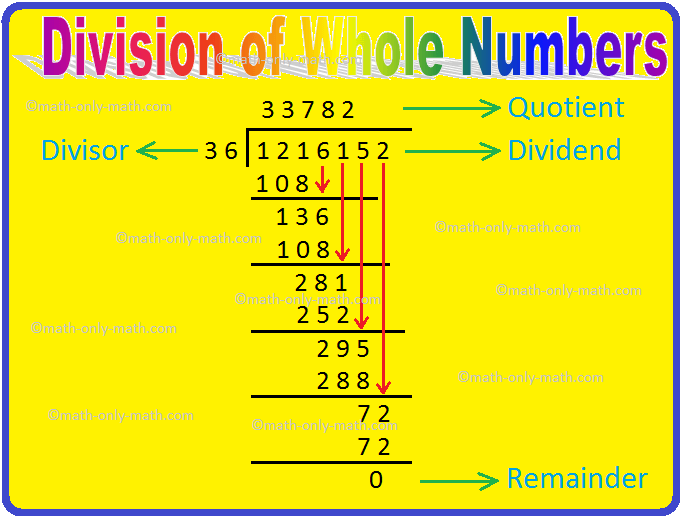
6 tens + 0 tens + 1 ten which is equal to 7 tens. 9 + 7 16 which is equal to 1 ten + 6 ones Step 2: Carry 1 ten to the tens column as shown. Solution: We arrange the given numbers in column and add as follows: Step 1: Add ones place i.e. Prime Number - A natural number greater than 1 which has only 1 and itself as factors. Solved Examples on Addition of Whole Numbers: 1. Any whole number that can divide exactly into another number, with nothing left over is a Factor. Definitions: Natural Numbers - Common counting numbers. I’ve probably already used a few words, that you are unfamiliar with.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
